BMI Calculator
The BMI calculator is a simple tool that gives a numerical value derived from an individual’s height and weight. It is widely used as a screening tool to categorize individuals into various weight categories such as underweight, normal, overweight, and obese.
Developed in the 19th century by Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet, BMI provides a general indication of body fatness, though it does not directly measure body fat percentage.
Indians are genetically more prone to abdominal fat and lifestyle diseases like diabetes and hypertension, even at lower BMI values. Therefore, Indian health authorities have defined stricter cutoffs to raise early awareness and prevent chronic conditions.
BMI Calculator
Calculate your Body Mass Index and get personalized health insights
Your Information
Your Results
Your BMI
--
Classification
--
BMI Prime
--
Ratio to upper normal BMI limit
Ponderal Index
--
kg/m³
Healthy Weight Range
--
For your height
Body Fat Estimate
--
Based on BMI and age
Advanced Health Metrics
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
--
Calories/day at rest
Daily Calorie Needs
--
Based on activity level
Waist-to-Height Ratio
--
--
Waist-to-Hip Ratio
--
--
Health Visualizations
Your Personalized Recommendations
Nutrition
Physical Activity
Lifestyle
Health Information
What is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measurement of a person's leanness or corpulence based on their height and weight. It is widely used as a general indicator of whether a person has a healthy body weight for their height. BMI is an attempt to quantify the amount of tissue mass in an individual, and then categorize that person as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese based on that value.
However, BMI has limitations as it does not account for differences in body composition, distribution of fat, or differences between populations.
BMI Categories
| Classification | BMI range (kg/m²) | BMI Prime | Health Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe Thinness | < 16.0 | < 0.64 | Severe |
| Moderate Thinness | 16.0 - 17.0 | 0.64 - 0.68 | Moderate |
| Mild Thinness | 17.0 - 18.5 | 0.68 - 0.74 | Mild |
| Normal | 18.5 - 25.0 | 0.74 - 1.0 | Minimal |
| Overweight | 25.0 - 30.0 | 1.0 - 1.2 | Increased |
| Obese Class I | 30.0 - 35.0 | 1.2 - 1.4 | High |
| Obese Class II | 35.0 - 40.0 | 1.4 - 1.6 | Very High |
| Obese Class III | > 40.0 | > 1.6 | Extremely High |
Additional Health Metrics
BMI Prime
BMI Prime is the ratio of a person's BMI to the upper limit of the "normal" BMI category (25 kg/m²). It simplifies BMI interpretation by showing how far a person's BMI is from the upper limit of normal.
Ponderal Index
The Ponderal Index (PI) is similar to BMI but uses the cube of height instead of the square. It is considered more accurate for very tall or short individuals.
Waist-to-Height Ratio
Waist-to-height ratio is an indicator of health risks associated with central obesity. A ratio of 0.5 or less is considered healthy.
Waist-to-Hip Ratio
Waist-to-hip ratio measures body fat distribution and is used to assess health risks. Higher ratios indicate more fat stored around the waist, which is associated with increased health risks.
Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage is the total mass of fat divided by total body mass. It is a more direct measure of body composition than BMI.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
BMR is the amount of energy expended while at rest. It represents the minimum amount of energy needed to keep your body functioning, including breathing and keeping your heart beating.
Limitations of BMI
While BMI is useful for population-level assessment, it has several limitations when applied to individuals:
- Does not distinguish between fat and muscle mass
- Does not account for differences in body composition between individuals
- May overestimate body fat in athletes and muscular individuals
- May underestimate body fat in older persons or those who have lost muscle mass
- Does not account for differences in body fat distribution
- Does not directly measure body fat percentage
- Can vary between different ethnic and racial groups
Health Risks
Risks of High BMI
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Cardiovascular disease
- Stroke
- Sleep apnea
- Certain types of cancer
- Osteoarthritis
- Gallbladder disease
- Fatty liver disease
- Mental health issues (depression, anxiety)
Risks of Low BMI
- Malnutrition
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Decreased immune function
- Hormonal imbalances
- Fertility problems
- Growth and development issues
- Increased risk of surgical complications
- Higher mortality risk in certain conditions
This calculator provides estimates and general information for educational purposes only.
It is not intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalized medical advice.
How a BMI Calculator Works
1. Inputs Required
- Weight (in Kg or lbs)
- Height (in cm, meters, or inches)
2. Computation
The formula (metric or imperial) is used to compute the BMI.
3. Result Display
The BMI value is displayed along with a category tag (e.g., “Normal”, “Overweight”).
BMI Formula
The BMI is calculated using the following formula:
In Metric Units:

In Imperial Units:
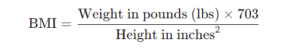
BMI Categories (Adults)
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), here are the standard BMI ranges:
| BMI Range | Classification |
|---|---|
| Less than 16 | Severely Underweight |
| 16 – 16.9 | Underweight |
| 17 – 18.4 | Mildly Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal Weight |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obese Class I |
| 35 – 39.9 | Obese Class II |
| 40 and above | Obese Class III |
Why Use a BMI Calculator?
A BMI calculator simplifies the process of assessing whether your weight falls within a healthy range. It can be used for:
- Personal health tracking
- Preliminary heathy assessments by doctors and nutritionists.
- Fitness planning and weight management.
- Health insurance eligibility and risk profiling.
FAQs on BMI Calculator
Q1. Is the BMI calculator accurate for everyone?
BMI is a general guideline and may not reflect body composition accurately, especially in athletes or the elderly.
Q2. Can I rely solely on the BMI calculator to assess my health?
No, it’s best used alongside other measurements, such as body fat percentage, waist circumference, and clinical assessments.
Q3. What’s a healthy BMI for Indians?
In India, a BMI between 18.5 to 22.9 is often considered normal, as per Indian council of Medical Research (ICMR) guidelines.
Q4. Is the BMI calculator useful for children?
Yes, but BMI-for-age percentile charts should be used.
Q5. How often should I check my BMI?
Check every few months or during routine health checkups, especially if you’re tracking weight-related goals.
Q6. Why do Indian BMI standards differ from global BMI charts?
Indians are genetically more prone to abdominal fat and lifestyle diseases like diabetes and hypertension even at lower BMI values. Therefore, Indian health authorities have defined stricter cutoffs to raise early awareness and prevent chronic conditions.
Q7. What’s the BMI range to plan for weight loss in India?
If your BMI is:
23 – 24.9: You are at risk. Moderate weight management is recommended.
25+: Weight loss through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes is strongly advised.
Q8. Can the BMI calculator help in pregnancy weight monitoring in India?
During pregnancy, BMI is used only before conception to assess risks.
- Underweight mothers may face nutritional deficiencies.
- Overweight/obese mothers may be at risk of gestational diabetes or delivery complications.
Post-conception, pregnancy-specific weight charts are used instead of BMI.
